Melanoma
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is the most deadly type of skin cancer. It arises from the disorganized growth and replication of cells in the skin that produce pigment or color (melanocytes). In the year 2019, there will be an estimated 96,000 new cases of melanoma diagnosed and approximately 7,500 people will die from the disease.
Unfortunately, incidence rates have slowly been on the rise over the past 10 years; however, with early detection and treatment, melanoma has a very high cure rate.
We ask all patients, whether you have light or dark skin, to perform self-examinations of their skin monthly. It has been well studied that early detection of melanoma is the most important indicator of prognosis.
Click HERE for information on how to do a self-skin exam at home.
When looking at your skin, it is helpful to keep in mind the ABCDEs of melanoma: asymmetry, border (irregular), color (varied instead of even), diameter (an increased risk if more than 6 mm, the size of a pencil eraser), evolving (changing moles are worrisome).
Normal Moles Vs. Melanoma
If you have any new or changing moles or growths on your skin, or if you have a mole or growth that is not healing or otherwise symptomatic, you should contact your dermatologist immediately. In addition to self-examinations, other behavioral modifications can also reduce your risk of melanoma.

Use these tips to protect your skin:
1). Avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak sun hours from 10am to 2pm. During this window, UV rays are at their strongest and can cause damage to your skin.
2). Generously apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends at least SPF 30 or higher with reapplication every 2 hours. You also need to reapply after sweating or swimming.
3). Wear sun protective clothing when possible. Many companies now make fashionable clothing and swimwear with SPF built right into the fabric!
4). Take caution around water, snow, and sand. The UV rays of the sun can reflect off of these and can be very damaging to skin.
5). NEVER, NEVER use an indoor tanning bed. Studies have shown with absolute certainty that these tanning beds increase your rate of both melanoma and non- melanoma skin cancers. They should never be used under any circumstances. Those who first use tanning beds in their youth increase their risk of melanoma by 75%. (https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/skin/basic_info/)
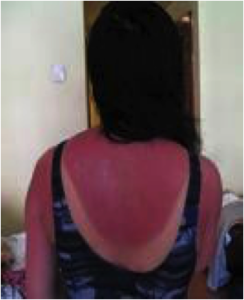
6). Protect your family. Outdoor tanning should also be avoided, as this can increase their risk for melanoma. The only safe tan is a fake tan from a bottle or spray! Sunburns, especially if they are blistering, can increase your chances of developing skin cancer.
Don’t believe us? Click THIS LINK for a very powerful video.
At Krauss Dermatology, we take skin cancer very seriously. If you have a lesion of concern, please call for an appointment to have it evaluated by a dermatologist.